AI and Science
Implications
AI and the transformation of social science research
Grossmann et al. (2023)
A well-summarized take. See also the extensive references, including an apparently exhaustive list of examples of AI in social sciences research.
LLMs can allow the kinds of simulations that until now were limited to domains that allowed numerical quantification – e.g. particle physics, epidemiology, economics. But with its ability to respond to surveys might make it a way to simulate research into human behavior.
Important caveat: “Already, LLM engineers have been fine-tuning pretrained models for the world that “should be” (12) rather than the world that is, and such efforts to mitigate biases in AI training (2, 13) may thus undermine the validity of AIassisted social science research.”
See ABM: Agent-based models are composed of: (1) numerous agents specified at various scales; (2) decision-making heuristics; (3) learning rules or adaptive processes; (4) an interaction topology; and (5) an environment.
via Penn Today
Software
GPT Researcher is an autonomous agent designed for comprehensive online research on a variety of tasks. (more details)
Elicit.org search scientific papers with AI
Paper-QA is a Github with examples for how to do scientific research reviews > minimal package for doing question and answering from PDFs or text files (which can be raw HTML). It strives to give very good answers, with no hallucinations, by grounding responses with in-text citations.
Lateral
 https://www.lateral.io/
https://www.lateral.io/
Complete hours of reading in minutes. A web app that helps you read, find, share & organise your research in one place. So you can complete it up to 10x faster.
Zeta Alpha
 https://www.zeta-alpha.com/ an Amsterdam-based company that claims “the best Neural Discovery Platform for AI and beyond. Use state-of-the-art Neural Search to improve how you and your team discover, organize and share knowledge.”
https://www.zeta-alpha.com/ an Amsterdam-based company that claims “the best Neural Discovery Platform for AI and beyond. Use state-of-the-art Neural Search to improve how you and your team discover, organize and share knowledge.”
see Sara Hamburg tweet.
https://www.scholarcy.com/
Scispace
I uploaded directly from my Zotero Library.
But when I asked it a basic question “What are the nutritional differences between frozen and fresh blueberries”
Worse, when I asked it:
“how does freezing impact the nutritional profile of blueberries”
The top answers related to electric vehicles, and “freezing” a pension plan.
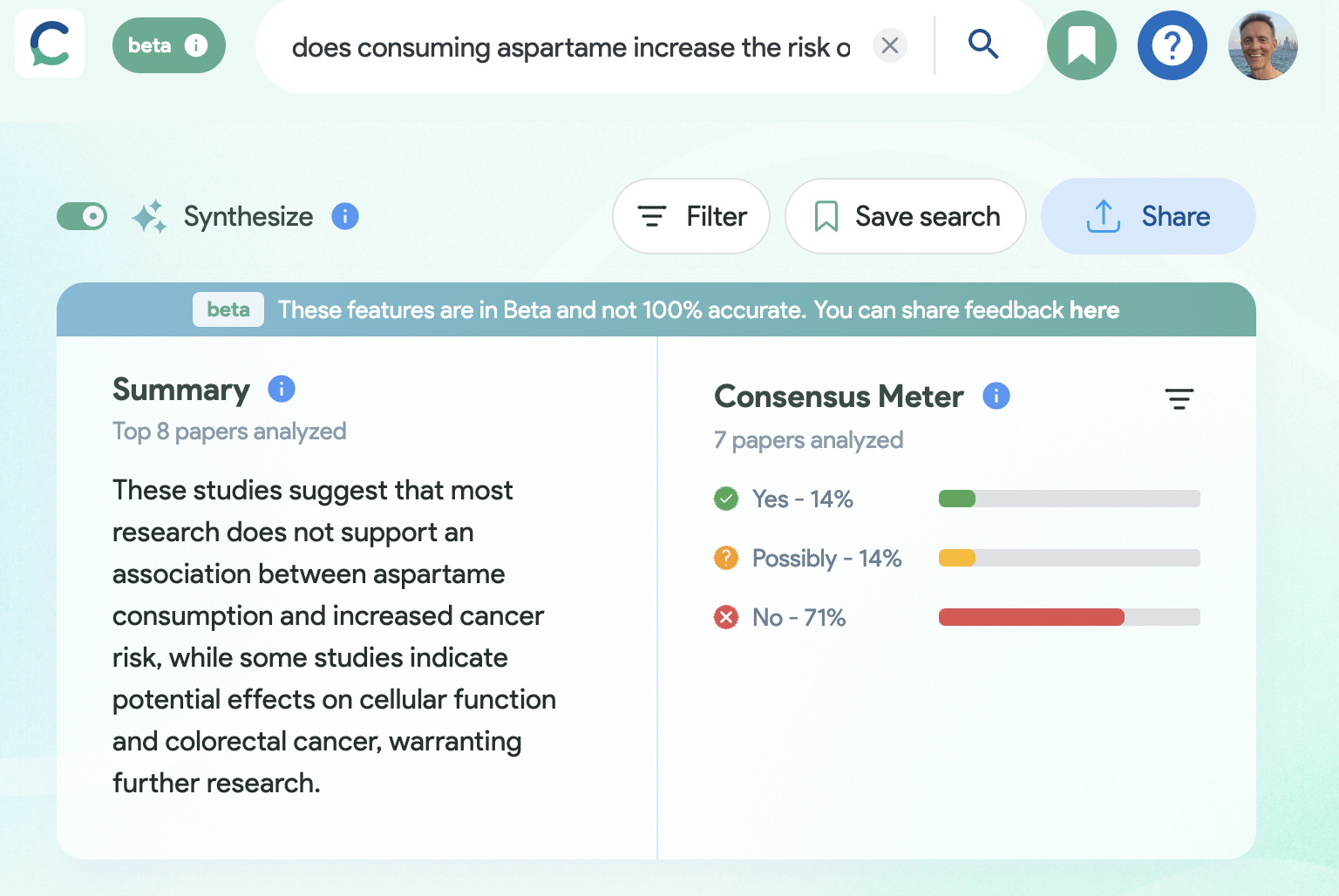
Consensus
Try “does consuming aspartame increase the risk of cancer?”
Scite_
1.2b citation statements extracted and analyzed 181m articles, book chapters, preprints, and datasets
Smart Citations allow users to see how a publication has been cited by providing the context of the citation and a classification describing whether it provides supporting or contrasting evidence for the cited claim 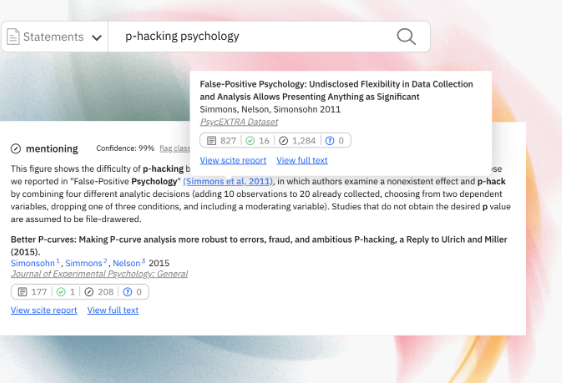
Discovery for science and beyond
Google’s FunSearch: Making new discoveries in mathematical sciences using Large Language Model
Romera-Paredes et al. (2024)
FunSearch works by pairing a pre-trained LLM, whose goal is to provide creative solutions in the form of computer code, with an automated “evaluator”, which guards against hallucinations and incorrect ideas. By iterating back-and-forth between these two components, initial solutions “evolve” into new knowledge. The system searches for “functions” written in computer code; hence the name FunSearch.